Navigating the Troublesome Seas of Wi-Fi Connection Problems in Laptops: A Comprehensive Guide
In today’s interconnected world, Wi-Fi connectivity has become an indispensable feature for laptops, enabling users to access the internet, communicate with others, and stream multimedia content from virtually anywhere. However, despite the ubiquity of Wi-Fi technology, users often encounter frustrating connectivity issues that disrupt their online activities and hinder productivity. From intermittent signal drops to slow connection speeds, Wi-Fi connection problems can stem from various factors and require careful diagnosis and troubleshooting to resolve effectively. In this extensive guide, we will delve into the common causes of Wi-Fi connection problems in laptops, explore potential solutions, and provide practical tips to help users overcome these challenges and enjoy seamless connectivity.
Understanding Wi-Fi Connection Problems:
Wi-Fi connection problems in laptops can manifest in several ways, including:
- Intermittent Signal Drops: The Wi-Fi connection may drop unexpectedly, requiring users to reconnect to the network repeatedly.
- Slow Connection Speeds: Despite a strong Wi-Fi signal, the internet connection may be slow or sluggish, affecting browsing, streaming, and downloading speeds.
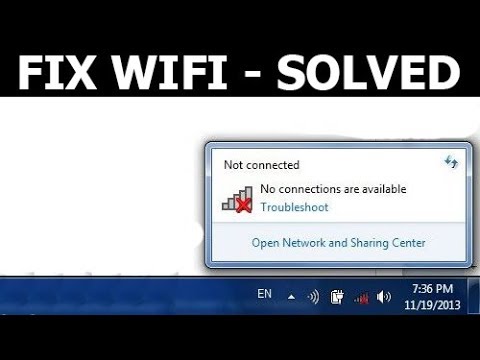
- Limited Connectivity: The laptop may display messages indicating limited or no connectivity to the Wi-Fi network, preventing access to the internet or local network resources.
- Inconsistent Performance: The Wi-Fi connection may exhibit inconsistent performance, with fluctuating signal strength or latency issues affecting network responsiveness.
Common Causes of Wi-Fi Connection Problems:
Wi-Fi connection problems in laptops can be attributed to various factors, including:
- Signal Interference: Interference from other electronic devices, neighboring Wi-Fi networks, or physical obstacles such as walls and furniture can disrupt Wi-Fi signals and cause connection problems.
- Outdated Drivers: Incompatible or outdated Wi-Fi adapter drivers can lead to connectivity issues as the laptop struggles to communicate with the wireless network effectively.
- Router Configuration Issues: Misconfigured router settings, including incorrect network security settings, channel congestion, or outdated firmware, can affect Wi-Fi performance and stability.
- Network Congestion: High levels of network traffic, particularly during peak hours, can overwhelm Wi-Fi networks and result in reduced connection speeds and performance.
- Hardware Malfunctions: Faulty hardware components, such as the Wi-Fi adapter or router, can cause connectivity problems due to hardware defects or damage.
Diagnosing and Troubleshooting Wi-Fi Connection Problems:
To diagnose and troubleshoot Wi-Fi connection problems in laptops, users can follow these steps:
- Check Wi-Fi Signal Strength: Verify the strength of the Wi-Fi signal on the laptop and ensure it is within range of the router or access point.
- Restart the Router: Power cycle the router by unplugging it from the power source, waiting for a few seconds, and then plugging it back in to reset the network settings and clear any temporary glitches.
- Update Wi-Fi Drivers: Update the Wi-Fi adapter drivers on the laptop to the latest version available from the manufacturer’s website or through the Device Manager in the Windows operating system.
- Adjust Router Settings: Access the router’s web interface and adjust settings such as the wireless channel, security mode, and transmission power to optimize Wi-Fi performance and minimize interference.
- Reset Network Settings: Reset the network settings on the laptop to default values to remove any conflicting configurations or settings that may be causing connectivity issues.
Practical Solutions to Wi-Fi Connection Problems:
Once the root cause of the Wi-Fi connection problem has been identified, users can implement the following solutions to address the issue:
- Optimize Router Placement: Position the router in a central location within the home or office, away from obstructions and electronic devices, to ensure optimal Wi-Fi coverage and signal strength.
- Upgrade Router Firmware: Check for and install firmware updates for the router from the manufacturer’s website to address known issues, improve performance, and enhance security.
- Use Wired Connection: Consider using a wired Ethernet connection for devices that require stable and high-speed internet access, particularly for activities such as online gaming or video streaming.
- Invest in Wi-Fi Range Extenders: Install Wi-Fi range extenders or repeaters to expand the coverage area of the Wi-Fi network and eliminate dead zones in larger homes or offices.
- Consult Technical Support: If Wi-Fi connection problems persist despite troubleshooting efforts, contact the internet service provider or router manufacturer for further assistance and guidance.
Conclusion:
Wi-Fi connection problems in laptops can be frustrating and disruptive, but with careful diagnosis and troubleshooting, they can often be resolved effectively. By understanding the common causes of Wi-Fi connection problems, performing diagnostic tests, and implementing practical solutions such as updating Wi-Fi drivers, adjusting router settings, and optimizing network placement, users can overcome connectivity issues and enjoy seamless Wi-Fi access on their laptops. With patience, persistence, and the right tools, users can navigate the troublesome seas of Wi-Fi connection problems and emerge victorious in their quest for reliable and stable internet connectivity.