Mastering Lighting Design with Dialux: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction: Lighting design plays a crucial role in creating aesthetically pleasing, functional, and energy-efficient environments across various architectural spaces, including residential, commercial, and industrial buildings. Dialux is a powerful software tool widely used by lighting designers, architects, and engineers to simulate, analyze, and visualize lighting solutions for interior and exterior spaces. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of using Dialux for lighting design, covering everything from project setup and luminaire selection to calculation methods and visualization techniques.
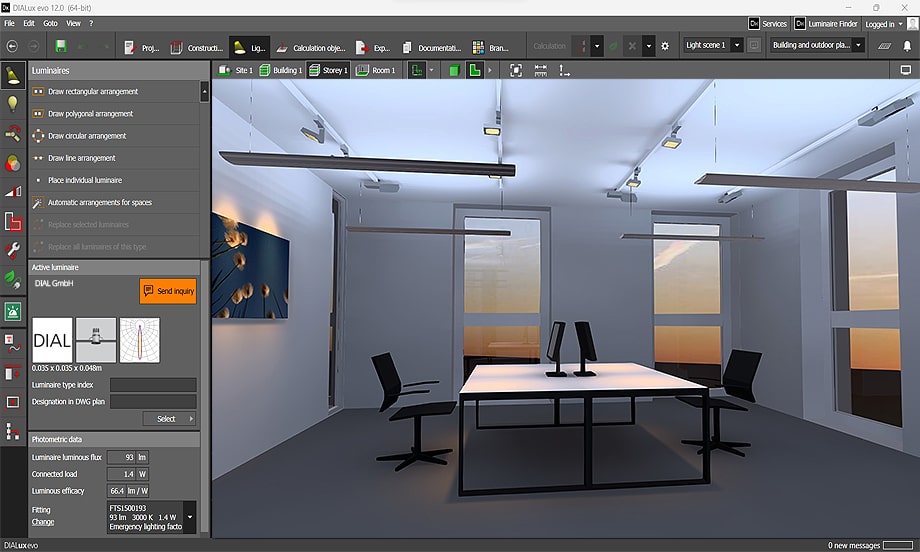
Section 1: Introduction to Dialux 1.1 Overview of Dialux: Dialux is a professional lighting design software developed by DIAL GmbH, a leading provider of lighting design solutions. It allows users to create photorealistic 3D visualizations of lighting installations, calculate lighting parameters such as illuminance and luminance, and optimize lighting designs for energy efficiency and visual comfort.
1.2 Importance of Lighting Design: Effective lighting design enhances the functionality, safety, and ambiance of architectural spaces while minimizing energy consumption and environmental impact. Lighting designers use Dialux to create lighting schemes that meet aesthetic, ergonomic, and regulatory requirements, ensuring optimal lighting quality and user satisfaction.
Section 2: Getting Started with Dialux 2.1 Installation and Setup: To begin using Dialux, users need to download and install the software from the official Dialux website. Once installed, users can launch the application and create a new project or open an existing one. Dialux provides a user-friendly interface with intuitive tools and menus for project management, luminaire selection, and scene creation.
2.2 Project Configuration: Before designing a lighting scheme in Dialux, users need to configure project settings such as location, room dimensions, and lighting standards. Users can specify the project location using geographical coordinates, set the room dimensions and surface properties, and define the lighting standards and calculation parameters according to project requirements.
Section 3: Luminaire Selection and Placement 3.1 Luminaire Database: Dialux provides a comprehensive database of luminaires from leading manufacturers, including architectural, decorative, and technical lighting fixtures. Users can browse the luminaire catalog, filter fixtures based on criteria such as type, application, and photometric properties, and select suitable luminaires for their lighting design projects.
3.2 Luminaire Placement: Once luminaires are selected, users can place them within the scene using Dialux’s intuitive drag-and-drop interface. Users can position luminaires accurately, adjust their orientation and tilt angles, and configure luminaire properties such as light distribution, intensity, and color temperature to achieve the desired lighting effect.
Section 4: Lighting Calculation and Analysis 4.1 Calculation Methods: Dialux offers various calculation methods for analyzing lighting parameters such as illuminance, luminance, and glare. Users can choose from point-by-point, grid-based, or ray tracing algorithms to calculate lighting levels and distributions within the scene, taking into account factors such as reflectance, daylight penetration, and luminaire characteristics.
4.2 Daylighting Analysis: In addition to artificial lighting, Dialux allows users to analyze daylighting conditions within the space and evaluate the interaction between natural and artificial light sources. Users can simulate daylight penetration, assess daylight availability and distribution, and optimize fenestration design and shading strategies to maximize daylight utilization and minimize energy consumption.
Section 5: Optimization and Energy Efficiency 5.1 Energy Consumption Analysis: Dialux enables users to assess the energy consumption of lighting installations and identify opportunities for energy savings. Users can analyze lighting power density, energy usage intensity, and lighting control strategies to optimize lighting designs for energy efficiency and compliance with sustainability standards such as LEED and BREEAM.
5.2 Lighting Control and Dimming: Dialux supports advanced lighting control features such as dimming, zoning, and scheduling to enhance energy savings and user comfort. Users can simulate lighting control scenarios, evaluate the impact of daylight harvesting and occupancy sensing on energy consumption, and design intelligent lighting systems that adapt to user needs and preferences.
Section 6: Visualization and Presentation 6.1 Photorealistic Rendering: Dialux offers photorealistic rendering capabilities for creating high-quality visualizations of lighting designs. Users can generate realistic renderings with accurate lighting effects, materials, and textures, and customize rendering settings such as resolution, exposure, and shadow quality to produce compelling presentations and client deliverables.
6.2 3D Visualization and Virtual Reality: In addition to static renderings, Dialux allows users to explore lighting designs in immersive 3D environments and virtual reality (VR) simulations. Users can navigate through the scene, interact with lighting fixtures in real time, and experience the visual impact of different lighting scenarios, enhancing design communication and stakeholder engagement.
Section 7: Documentation and Reporting 7.1 Lighting Layouts and Plans: Dialux generates comprehensive documentation and reports for lighting design projects, including lighting layouts, plans, and schedules. Users can create 2D layout drawings with luminaire positions, room dimensions, and lighting calculations overlaid, as well as detailed luminaire schedules with specifications such as wattage, color temperature, and mounting height.
7.2 Compliance Documentation: Dialux assists users in generating compliance documentation for regulatory and certification purposes, such as lighting compliance reports and documentation for building permit applications. Users can demonstrate compliance with lighting standards and regulations, verify design intent, and communicate lighting requirements to project stakeholders and regulatory authorities.
Section 8: Real-World Applications and Case Studies 8.1 Architectural Lighting Design: Dialux is widely used in architectural lighting design for illuminating interior and exterior spaces, including offices, retail stores, museums, and public buildings. Lighting designers use Dialux to create dynamic lighting schemes that enhance architectural features, improve visual comfort, and create memorable experiences for occupants and visitors.
8.2 Outdoor Lighting and Landscape Design: In outdoor lighting and landscape design, Dialux is employed to illuminate streets, parks, plazas, and other public spaces. Lighting designers use Dialux to simulate lighting effects, assess glare and light pollution, and optimize luminaire placement and aiming angles to enhance safety, security, and nighttime aesthetics in outdoor environments.
Section 9: Best Practices and Optimization Strategies 9.1 Collaborative Design Workflow: To streamline the lighting design process, teams can adopt a collaborative workflow using Dialux’s project sharing and collaboration features. Teams can work together on the same project, share design data and resources, and collaborate in real time to develop cohesive lighting solutions that meet project objectives and client expectations.
9.2 Continuous Learning and Professional Development: To stay abreast of the latest trends and techniques in lighting design, users should invest in continuous learning and professional development opportunities. DIAL GmbH offers training courses, webinars, and certification programs for lighting designers and engineers seeking to enhance their skills and proficiency in Dialux and lighting design principles.
Section 10: Future Trends and Developments 10.1 Advanced Simulation and Analysis: Future versions of Dialux may incorporate advanced simulation and analysis capabilities for predicting lighting behavior in complex environments. Engineers may leverage ray tracing, radiosity, and global illumination algorithms to simulate realistic lighting effects, such as reflections, refractions, and caustics, and achieve greater accuracy and realism in lighting design simulations.
10.2 Integration with Building Information Modeling (BIM): As building information modeling (BIM) continues to gain traction in the AEC industry, Dialux may integrate with BIM platforms to enable seamless data exchange and interoperability between lighting design and building design disciplines. Integration with BIM tools such as Autodesk Revit and Trimble SketchUp would facilitate the synchronization of lighting layouts, room geometries, and building elements, streamlining the design coordination and documentation process.
Conclusion: Dialux is a versatile and powerful tool for lighting designers, architects, and engineers seeking to create innovative, energy-efficient, and visually compelling lighting solutions for architectural spaces. By mastering the techniques and best practices outlined in this guide, users can leverage Dialux’s advanced features and capabilities to develop lighting designs that enhance occupant comfort, improve energy efficiency, and elevate the aesthetic quality of built environments. With its intuitive interface, robust calculation engine, and photorealistic visualization tools, Dialux continues to be a preferred choice for lighting professionals worldwide, driving innovation and excellence in lighting design across diverse industries and applications.