How to manage virtual hard disks in Windows 8
Managing virtual hard disks (VHDs) in Windows 8 is crucial for various tasks such as creating, attaching, detaching, and configuring virtual drives for virtual machines and other purposes. Virtual hard disks serve as containers for storing operating systems, applications, and data in a virtualized environment, allowing users to efficiently manage and deploy virtualized workloads. Whether you’re a system administrator, developer, or power user, understanding how to manage virtual hard disks in Windows 8 is essential for effective virtualization and system management. In this extensive guide, we’ll delve into everything you need to know about managing virtual hard disks in Windows 8, covering topics such as creating VHDs, attaching and detaching them, resizing and converting them, and optimizing their performance for various use cases.
Understanding Virtual Hard Disks:
Virtual hard disks (VHDs) are disk image files that emulate physical hard disks in a virtualized environment. VHDs are commonly used in virtualization platforms such as Hyper-V to store operating system images, applications, and data for virtual machines. In Windows 8, users can create and manage VHDs using built-in tools and utilities, enabling them to deploy, configure, and maintain virtualized workloads with ease.
Creating Virtual Hard Disks:
To create a virtual hard disk in Windows 8, follow these steps:
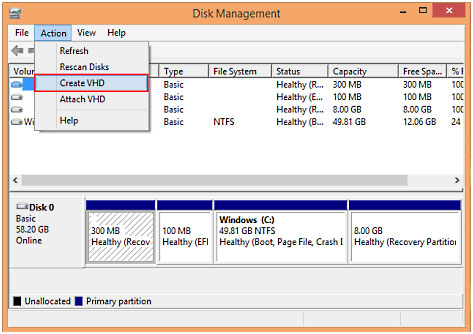
- Open Disk Management: Press the Windows key to open the Start menu, then type “Disk Management” in the search bar. Click or tap on “Create and format hard disk partitions” in the search results to launch Disk Management.
- Create VHD: In Disk Management, click or tap on “Action” in the menu bar, then select “Create VHD.” Specify the location, size, and format options for the VHD, then click or tap on “OK” to create the VHD.
- Initialize and Format: After creating the VHD, right-click on the disk in Disk Management and select “Initialize Disk.” Choose the partition style (MBR or GPT), then right-click on the unallocated space and select “New Simple Volume” to format the VHD.
Attaching and Detaching Virtual Hard Disks:
To attach a VHD in Windows 8, follow these steps:
- Open Disk Management: Launch Disk Management as described above.
- Attach VHD: In Disk Management, click or tap on “Action” in the menu bar, then select “Attach VHD.” Browse to the location of the VHD file, select it, then click or tap on “OK” to attach the VHD.
To detach a VHD in Windows 8, follow these steps:
- Open Disk Management: Launch Disk Management as described above.
- Detach VHD: In Disk Management, right-click on the attached VHD and select “Detach VHD.” Confirm the action when prompted, then click or tap on “OK” to detach the VHD.
Resizing and Converting Virtual Hard Disks:
To resize a VHD in Windows 8, follow these steps:
- Open Disk Management: Launch Disk Management as described above.
- Extend or Shrink VHD: Right-click on the VHD in Disk Management and select “Extend Volume” or “Shrink Volume,” depending on whether you want to increase or decrease the size of the VHD. Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the resizing operation.
To convert a VHD between fixed and dynamically expanding formats in Windows 8, you can use the Convert-VHD PowerShell cmdlet. For example, to convert a VHD named “Disk.vhd” to a dynamically expanding format, you would use the following command:
Convert-VHD -Path "C:\Path\To\Disk.vhd" -DestinationPath "C:\Path\To\NewDisk.vhdx" -VHDType Dynamic
Optimizing Virtual Hard Disks Performance:
To optimize the performance of virtual hard disks in Windows 8, consider the following tips:
- Use Fixed-size VHDs: Fixed-size VHDs offer better performance compared to dynamically expanding VHDs, as there is no overhead associated with dynamically allocating storage space.
- Use SCSI Controllers: When attaching VHDs to virtual machines, consider using SCSI controllers instead of IDE controllers for better performance and scalability.
- Enable Hyper-V Integration Services: If you’re using Hyper-V virtual machines, ensure that Hyper-V Integration Services are installed and enabled on the guest operating system to improve performance and functionality.
- Use SSD Storage: Consider storing VHD files on solid-state drives (SSDs) for improved performance, especially for I/O-intensive workloads.
Conclusion:
Managing virtual hard disks in Windows 8 is essential for effective virtualization and system management. Whether you’re creating, attaching, detaching, resizing, or optimizing virtual hard disks, understanding how to perform these tasks ensures that you can efficiently manage virtualized workloads and environments. By following the steps and tips outlined in this guide, users can leverage the built-in tools and utilities in Windows 8 to create, configure, and maintain virtual hard disks with ease. With virtual hard disks, users can take advantage of the flexibility, scalability, and efficiency of virtualization to meet their computing needs and requirements effectively.