SkyDrive Integration: Seamlessly Syncing Your Digital World with Windows 8
In the ever-evolving landscape of operating systems, Microsoft’s Windows 8 brought a slew of innovations to the forefront, redefining the user experience in the digital realm. One of the standout features that played a transformative role in how users managed their digital content was the seamless integration of SkyDrive, Microsoft’s cloud storage service. This article takes an in-depth look at how SkyDrive integration became a cornerstone of Windows 8, facilitating effortless synchronization of files and ushering in a new era of digital accessibility and collaboration.
1. The Genesis of SkyDrive Integration: Windows 8, released in 2012, introduced a paradigm shift by incorporating cloud integration as a core element of the operating system. SkyDrive, previously a standalone service, was seamlessly woven into the fabric of Windows 8. The integration aimed to address the evolving needs of users who increasingly sought flexible and accessible solutions for managing their digital content across devices.
2. Access Anywhere, Anytime: Breaking the Tether of Local Storage: SkyDrive integration empowered users to break free from the constraints of local storage. Files stored in the cloud were accessible from any device with an internet connection, providing a level of flexibility and convenience that resonated with the increasingly mobile-centric user base. Whether at home, in the office, or on the go, Windows 8 users could seamlessly access their files, fostering a sense of continuity in their digital experience.
3. User-Friendly Setup: Integrating SkyDrive into the Operating System: Microsoft ensured that integrating SkyDrive into the Windows 8 experience was a user-friendly process. From the initial setup to ongoing usage, the integration was seamless. Users could sign in with their Microsoft account, and SkyDrive would automatically sync their files, making them accessible across devices with minimal effort.
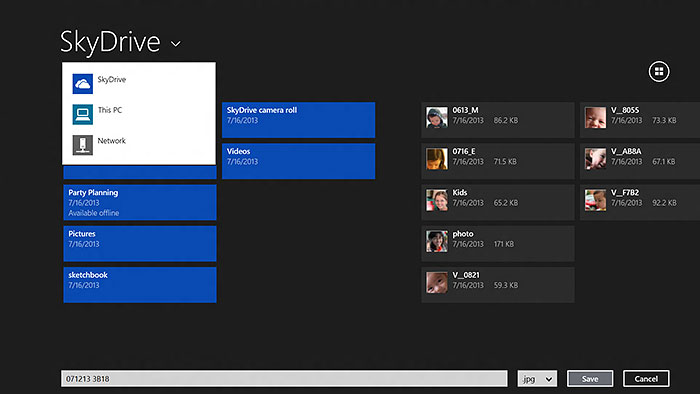
4. SkyDrive App: A Centralized Hub for Cloud Management: Windows 8 featured a dedicated SkyDrive app, providing users with a centralized hub for managing their cloud-stored content. The app offered a visual representation of files and folders, making it easy for users to organize, upload, and download content directly from their devices.
5. File Synchronization: Real-Time Updates Across Devices: One of the key advantages of SkyDrive integration was the real-time synchronization of files across devices. Changes made on one device were instantly reflected on all connected devices. This seamless synchronization ensured that users always had access to the latest version of their files, irrespective of the device they were using.
6. Office Integration: Collaborative Productivity in the Cloud: SkyDrive wasn’t just about storing files; it was intricately woven into the Microsoft Office suite, enhancing collaborative productivity. Users could create, edit, and share documents, presentations, and spreadsheets directly from the cloud. The integration with Office apps ensured that collaboration was not hindered by geographical boundaries.
7. Fetch Files: Bridging the Gap Between Devices: Windows 8 introduced a novel feature called “Fetch Files” that extended the reach of SkyDrive. Users could access files from their connected devices remotely, bridging the gap between home and office environments. This feature added an extra layer of convenience, allowing users to retrieve important documents even if they forgot to store them in the cloud explicitly.
8. Photos and Videos: Immersive Media Experience in the Cloud: SkyDrive integration extended beyond documents to encompass multimedia files. Users could store and organize their photos and videos in the cloud, creating an immersive media experience that transcended individual devices. This feature became particularly valuable for users who wanted to share and showcase their media collections seamlessly.
9. Automatic Camera Roll Backup: Effortless Preservation of Memories: With the integration of SkyDrive, Windows 8 introduced automatic Camera Roll backup. Users’ photos and videos captured on their devices were automatically uploaded to the cloud, ensuring that precious memories were preserved without manual intervention. This feature exemplified the commitment to making digital life more convenient and secure.
10. Selective Sync: Tailoring Cloud Storage to User Needs: Recognizing that users might not want to sync their entire SkyDrive library to every device, Windows 8 introduced selective sync. This feature allowed users to choose specific folders to sync, tailoring their cloud storage to their unique needs and optimizing storage space on individual devices.
11. Security and Privacy: Safeguarding User Data in the Cloud: With the shift to cloud-centric storage, security and privacy concerns were paramount. Windows 8 addressed these concerns by implementing robust security measures for SkyDrive. Data transmission was encrypted, and users had control over sharing permissions, ensuring that their sensitive information remained secure in the cloud.
12. SkyDrive for Developers: Extending Functionality through APIs: Windows 8 encouraged third-party developers to leverage SkyDrive through application programming interfaces (APIs). This openness expanded the functionality of SkyDrive, allowing developers to integrate cloud storage seamlessly into their applications, fostering a more interconnected and versatile digital ecosystem.
13. Windows 8.1 and Further Refinements: Listening to User Feedback: Microsoft’s commitment to refining the user experience was evident in the Windows 8.1 update. Based on user feedback, SkyDrive underwent further refinements, enhancing performance, introducing new features, and ensuring that the cloud integration remained a cornerstone of the Windows 8 experience.
14. Rebranding to OneDrive: A Continuation of the Cloud Journey: In subsequent years, Microsoft rebranded SkyDrive to OneDrive, ushering in a new era while retaining the core principles of seamless cloud integration. The rebranding reflected the evolution of cloud services and Microsoft’s ongoing commitment to providing users with a unified and accessible cloud storage solution.
15. Legacy and Ongoing Impact: Shaping the Future of Cloud Integration: The integration of SkyDrive into Windows 8 left an indelible mark on the evolution of operating systems. It not only shaped the user experience of Windows 8 users but also influenced the broader industry’s approach to cloud integration. The lessons learned from the seamless synchronization of digital content continue to resonate in contemporary operating systems and cloud services.
16. Conclusion: Transforming Digital Accessibility: In conclusion, SkyDrive integration in Windows 8 represented a transformative leap in how users interacted with their digital content. The seamless synchronization of files across devices, coupled with collaborative productivity features, elevated the user experience to new heights. As technology continues to advance, the legacy of SkyDrive integration endures as a testament to Microsoft’s vision of a connected, accessible, and user-centric digital future.